IoT presents a number of technical challenges. Here’s how cloud computing helps solve them.
Distinctively two separate technologies, the Internet of Things (IoT) and cloud computing are closely associated.
When the two are combined, they deliver powerful innovation that will continue to alter how we interact with our devices and with one another, and change how we store, manage and consume information.
IoT can potentially transform your business by allowing you to develop smarter products and services, collect data that will influence your business decisions, and possibly alter your business model to enhance growth and expansion.
Labeled as “the next Industrial Revolution”, the Internet of Things will continue to transform the way we live, as well as how you interact with your employees, customers, and assets.
And cloud computing will be the backbone of everything IoT has to offer.
Overview of the Internet of Things
Before we jump into how IoT and the cloud work together, let’s first define IoT and take a look at the industry as whole.
The Internet of Things refers to the extension of network connectivity and computing capability to objects, devices, sensors, and items not ordinarily considered to be computers.
These things are many times referred to as “smart objects” and require minimal human intervention to generate, exchange, and consume data. They often feature connectivity to facilitate remote data collection, analysis, and management.
Iot Product Examples
The most popular IoT products are consumer goods that you may already own.
The Nest thermostat collects data on and adapts to your climate preferences so you don’t have to constantly adjust the temperature of your heat or air conditioning.
Amazon Echo lets you control your music, lights, and other components of your home with your voice.
Fitbit and other fitness trackers allow you to monitor your physical activity, sleep patterns, and more. Smartwatches like Apple Watch and Android Wear let you read emails, play games, and more, right on your wrist.
But that’s not even the half of it. IoT products are everywhere in enterprises and the government.
Healthcare is an industry where innovative IoT applications are being developed.
Stanley Healthcare’s AeroScout® Real-Time Location System platform gives hospitals visibility to the status and location of patients, staff, and equipment. And Kinsa built smart thermometers that take accurate readings, track medical history for each member of your family, and offer guidance on next steps if your temperature is abnormal.
Governments are leveraging smart city applications, such as connected meters, sensors, and lights, to collect and analyze data and help solve issues such as pollution, traffic gridlock, and energy consumption.
For instance, Big Belly’s trash compactor has sensors that identify when the can is getting full and then will compact the trash so there’s room for more garbage.
Smart objects are all around us, and there will be more and more to come.
IoT Market By the Numbers
The IoT industry is expected to explode over the next few years and beyond.
From smart home devices and connected cars, to the development of smart cities and more efficient businesses, Gartner predicts 21 billion connected things will be in use by year 2020.
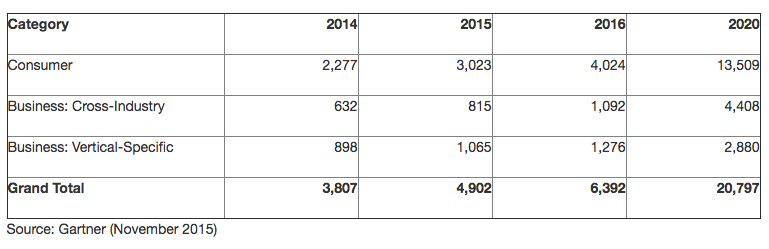
These 21 billion things will be built, used, and embraced by three primary entities – consumers, governments and businesses.
Each entity will spend a considerable amount on building and using IoT products by the end of 2020. Consumers are predicted to spend over $900 million on IoT products, while governments and businesses will spend $2.1 billion and $3 billion, respectively.
And much of this industry is powered by cloud computing.
How Cloud Computing can Solve IoT’s Challenges
The growth of IoT will put a strain on the computing resources necessary to maintain the level of connectivity and data collection that IoT devices require.
Cisco predicts that global machine-to-machine IP traffic will grow nearly sixfold from 1.6 exabytes (1 exabyte = 1 billion gigabytes!) per month in 2016 to 6.3 by 2020. Much of this will be attributed to IoT devices.
Other issues, such as product development challenges, scalability, security, and more, will arise.
How can you possibly deal with the level of resources needed to launch an IoT product?
That’s where cloud computing can help.
Below, we identify these challenges and offer insight into how the cloud helps resolve these issues.
1) There are many technical hurdles to deploying an IoT solution; the cloud eases some of these burdens and accelerates development.
It’s not easy to launch an IoT solution.
First, you have to worry about how your hardware or machinery will function. This can entail working with sensors, connecting the hardware to the internet, potentially dealing with battery life, and more.
Then you have to develop the software to facilitate all of the communication and data collection.
Finally, you have to deploy all of the back-end infrastructure to bring all of the moving parts of your IoT solution together.
Cloud computing can help you deal with these technical issues.
When you’re developing your IoT hardware and software, you don’t want to have to worry about setting up servers, deploying databases, configuring networks, and performing many other infrastructure tasks.
Cloud computing providers have all of this ready at a moment’s notice. You can easily spin up virtual servers, launch a database instance, and create data pipelines to help run your IoT solution.
What’s more, there are now services specifically dedicated to launching and managing IoT offerings.
For instance, AWS’s IoT platform allows you to easily and securely connect devices to one another, manage these connections, and capture and feed collected data into other AWS technologies like S3 and Redshift for processing and analysis.
Not only will this help speed up your development process, but it can also cut down on development costs. You won’t have to spend money upfront to purchase and provision servers and other infrastructure, and you’ll only pay for the resources that you consume.
Because cloud computing providers already have all of the infrastructure that you need, they can help speed up your development process, get to market faster, and allow you to focus on building the best product possible.
2) IoT devices can deliver massive amounts of data and use infrastructure resources in an inconsistent manner; the cloud can provide the scalability and flexibility to deal with this.
IoT traffic and the number of devices are set to erupt over the next few years, leading to increased interactions between devices and huge volumes of data generated.
This means your business will need a cost-efficient way to store, process, and access data from your IoT solutions and scale resources to handle peaks of demand when necessary.
With cloud computing, you can set up your infrastructure capacity to instantly scale up when usage increases and drop down when demand is lower. If you use traditional servers, you would have to buy enough capacity to account for peak times, which would then sit idle at times of low use and continue to subtract from your bottom line.
Additionally, as you add more features into your IoT solution, you can easily scale the infrastructure to handle all of this functionality.
Take John Deere for example. The agriculture giant is paving the way for farmers to leverage IoT to better understand their farms and be smarter about their output.

They’ve built smart farm solutions that facilitate real-time monitoring, control, and analysis of activities such as land preparation, seeding, fertilizing, and harvesting.
These include the SeedStar Mobile application, which provides real-time, row-by-row planting performance data.
JDLink is another mobile application that allows farmers and their machinery dealers to access fleet location, utilization, fuel usage, and diagnostic data for each machine remotely and in real time.
All of these applications are powered by cloud computing so they can handle the fluctuating demands of farmers accessing and monitoring various amounts of data, at any given time, from any device and location.
And as John Deere continues to build out its portfolio of IoT solutions, they can easily scale their infrastructure resources to accommodate new apps and the customers that use them.
3) Data security will always be a concern in IoT; the cloud can help improve security for your solution.
With the growth of the IoT industry comes plenty of security challenges.
It’s already difficult to secure your employees’ computers, mobile phones, and other devices. Imagine how difficult it can be to secure thousands of other devices that are in the hands of unsuspecting users?
Each of these devices can be the portal into the sensitive information of your customers, employees, and lines of business, and access to this data can lead to stolen identities, loss of money, and even bodily harm.
Because many smart devices are interconnected, it may only take a breach at a single point to gain access to an entire IoT ecosystem. Scary.
A few high-profile IoT security breaches have already occurred.
Chrysler recalled 1.4 million Jeeps due to a security flaw, the Tesla Model S entertainment system was hacked, and up to 2.2 million BMW-built vehicles were susceptible to a breach that could let hackers unlock the cars’ doors.
A hack of VTech’s Learning Lodge app store databases exposed the data of 6.4 million children.
And a breach of digital video recorders and internet-connected cameras led to massive internet outages last October.

All of these security breaches prompted the Cloud Security Alliance to create guidelines that identify the key actions that should be taken to ensure the security of an IoT offering.
IoT security starts with educating the end user of the risks involved and how they can protect themselves.
After that, the cloud can help secure the smart device itself and the backend that powers all of these devices.
Below are some tactics that will help secure your IoT offering and how the cloud can help facilitate them.
Authentication
The first line of defense is proper authentication of users at the device level.
Every cloud provider has an identity management solution that can and should be integrated into your IoT solution so users can log into their devices safely and securely.
For instance, AWS has Identity and Access Management (IAM) and Cognito modules to help facilitate secure login and access.
Additionally, certificates should be issued to each device so information about potential security breaches, such as when the breach occurred, where the device was located, and more, can be captured and analyzed. Also, these certificates can be revoked so the device is no longer connected to the IoT ecosystem once it has been stolen or compromised, further ensuring security of your environment.
Firmware and Software Update Procedures
A standard process for ensuring that your IoT devices have the most recent firmware and software should be created on day one.
Devices with outdated firmware and software are prime targets for hackers, who know that the devices and ecosystems without the latest security patches are the most vulnerable.
Cloud providers have tools and processes that allow for easy setup of Firmware-Over-The-Air (FOTA) and software updates. Also, these updates can be signed with digital certificates that let your users know that they are secure and legitimate.
Encryption
With the amount of data that’s created by smart devices, it may be difficult to identify signals of suspicious activity and separate them from all of the noise.
Hackers know this, and it’s a major reason why they target IoT environments.
Thus, it’s imperative to encrypt as much data as possible that flows throughout your IoT ecosystem and is stored in your databases.
Cloud platforms can help you manage both client- and server-side encryption, automate the encryption process, and create customized encryption solutions that fit your company’s security policies.
And cloud security experts always stay on top of the latest threats and trends so you don’t have to.
Check out this article that highlights the important criteria for encrypting your data in the cloud. No matter how much data you decide to encrypt, the cloud will be an important tool in helping you do so.
[thrive_leads id=’8366′]
4) Lack of integration and interoperability is holding back the true potential of IoT. The cloud can help IoT devices work better with your current systems and with each other.
To get the true value out of your IoT solution, it’s best to seamlessly integrate the data you’re collecting from these devices with the information you have in current business applications.
For instance, if you run a manufacturing company and are gathering uptime data from sensors on your machines, you can link this information with your shipping logs to identify the impact of machine downtime on delivery times.
But often these data sets are siloed on separate servers and inaccessible to be analyzed in tandem.
The cloud can help link applications and processes, and house all of these data so they can be seamlessly integrated and analyzed, regardless of the source.
Additionally, the cloud can help your IoT solution better integrate with the smart products built by other companies, which can ultimately provide more value to your users.
Because the IoT industry is still in its infancy, there are many companies trying to build their own platform with the goal of becoming the market leader.
This has led to a lack of standards where devices from different manufacturers can’t communicate with each other, devices that run on multiple operating systems can’t be integrated, and data can’t be shared across platforms.
This fragmentation is a big problem that’s holding back the true potential of IoT, but a few companies are working on cloud solutions that alleviate issues with interoperability.
Intel released an IoT platform reference architecture alongside hardware and software products that aim to standardize the complex and fragmented IoT industry.
IBM has also made a push towards solving the lack of interoperability by collaborating with global alliances and working groups such as the Cloud Standards Customer Council and the Distributed Management Task Force to develop standards and build a cloud environment that interoperates smoothly with the majority of applications, appliances, and platforms.
In order for IoT to reach its full potential, connectivity and communication between things, people, and processes is needed, no matter who makes the devices. And cloud computing will play an important role in bringing it all together.
Conclusion
IoT promises to connect all things – people, computers, devices and networks – but the promise cannot be fulfilled without the integration of the cloud.
The cloud can help you develop your IoT products faster; deal with all of the data that these products generate and infrastructure resources they may use; secure your IoT ecosystem; and better integrate your devices with your current systems and other IoT devices.
The cloud is an essential part of a successful IoT environment and should play a major role in your development or improvement of IoT products.
What are your thoughts about how the cloud can help power your IoT products and the industry as a whole? We’d love to hear from you in the comments.



